More Than Just "Stress" – The Power of Cortisol
We often hear about "cortisol" in hushed tones, usually associated with stress and its negative impacts. While it's true that cortisol is your body's primary "stress hormone," that label only tells half the story. Cortisol is a vital steroid hormone, a natural chemical messenger, produced by your adrenal glands (two small glands nestled atop your kidneys). It's a fundamental player in countless bodily functions, helping you wake up, manage energy, fight inflammation, and yes, navigate stressful situations.
Understanding cortisol isn't just about avoiding stress; it's about appreciating a sophisticated system that keeps you alive and thriving. Let's delve into the fascinating world of cortisol, uncovering its crucial roles, how it's regulated, and what happens when its delicate balance is disturbed.
Table of Contents
What Exactly Is Cortisol? Your Body's Master Regulator
Imagine your body has an internal alarm system, ready to react to any perceived threat or demand. Cortisol is the primary messenger in that system. When your brain senses stress – whether it's a looming deadline, a physical injury, or even just your morning alarm – it triggers a cascade of events that culminates in the release of cortisol.
This hormone then acts like a conductor, orchestrating various bodily responses to ensure you have the energy and resources to cope. It's not inherently "bad"; in fact, it's essential for survival. Without cortisol, your body wouldn't be able to handle stress, regulate blood sugar, or even maintain blood pressure effectively.
The Multifaceted Roles of Cortisol: Beyond "Fight or Flight"
While its role in the "fight or flight" response is widely known, cortisol performs a much broader spectrum of duties throughout your body:
- Stress Response Maestro:
- Acute Stress: When you face immediate danger or a sudden challenge, cortisol floods your system. It rapidly increases your heart rate, blood pressure, and directs blood flow to your muscles, providing a burst of energy and heightened awareness. This is your evolutionary advantage, preparing you to run or fight.
- Chronic Stress: In modern life, stress is often persistent rather than acute. Cortisol continues to be released, keeping your body in a state of high alert. While beneficial in short bursts, prolonged elevation can have significant health consequences.
- Metabolic Powerhouse:
- Blood Sugar Regulation: One of cortisol's most critical roles is maintaining stable blood glucose levels. It signals your liver to produce more glucose (a process called gluconeogenesis) and makes your cells less sensitive to insulin. This ensures a steady supply of energy for your brain and muscles, especially during times of fasting or stress when food intake is low.
- Fat and Protein Metabolism: Cortisol also influences how your body uses fats and proteins. It can promote the breakdown of stored fat and muscle protein, converting them into energy when needed.
- Anti-Inflammatory Agent:
- Cortisol possesses powerful anti-inflammatory properties. In the short term, it helps to dampen the immune system's inflammatory response, preventing it from overreacting. This is why synthetic cortisol (corticosteroids) is a common medication for conditions like asthma, allergies, and arthritis. However, chronic high cortisol can ironically lead to increased inflammation over time.
- Blood Pressure Maintenance:
- Cortisol works to maintain stable blood pressure and supports overall cardiovascular function. It helps regulate the tone of blood vessels and the volume of fluids in your body.
- Immune System Modulator:
- While it can suppress certain immune functions (as mentioned with inflammation), cortisol also plays a role in regulating the immune system's balance. Prolonged elevated cortisol, however, can weaken your immune defenses, making you more vulnerable to illness.
- Sleep-Wake Cycle Conductor (Circadian Rhythm):
- Cortisol levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day in a predictable pattern called the circadian rhythm. They are typically highest in the early morning, helping you feel awake and alert, and gradually decline throughout the day, reaching their lowest point around midnight, which helps prepare you for sleep. This rhythmic release is crucial for a healthy sleep-wake cycle.
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance:
- It helps regulate the balance of sodium and water in your body, contributing to kidney function and overall hydration.
The HPA Axis: How Cortisol is Regulated
The production and release of cortisol are under the strict control of a sophisticated communication network known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. This intricate feedback loop involves three key players:
- Hypothalamus (in your brain): Detects stress or low cortisol levels and releases Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH).
- Pituitary Gland (also in your brain): In response to CRH, the pituitary releases Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH).
- Adrenal Glands (on top of your kidneys): Stimulated by ACTH, the adrenal glands produce and release cortisol.
Once cortisol levels rise in the bloodstream, they send signals back to the hypothalamus and pituitary, telling them to reduce the release of CRH and ACTH. This negative feedback loop ensures that cortisol levels don't get too high and helps maintain a healthy balance.
When Cortisol Levels Go Awry: Imbalances and Health Impacts
While essential, too much or too little cortisol can lead to significant health problems.
- Too Much Cortisol (Hypercortisolism):
- Often associated with Cushing's Syndrome, which can be caused by tumors (on the pituitary or adrenal glands), long-term use of corticosteroid medications, or chronic, unmanaged stress.
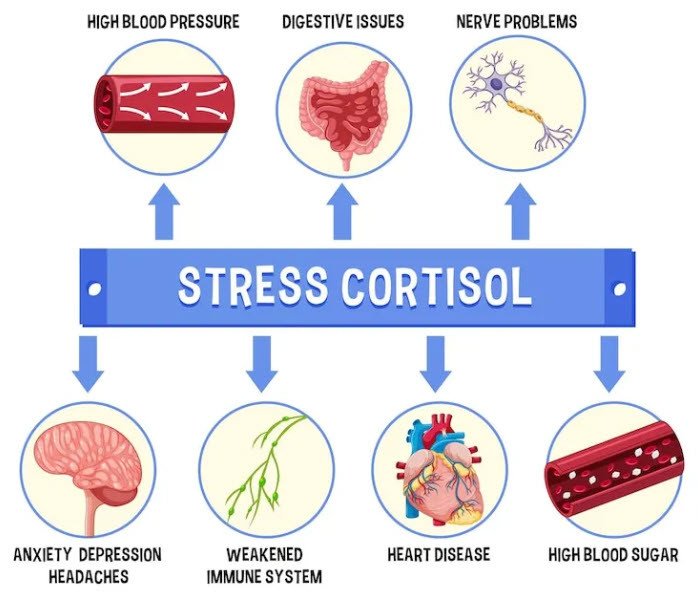
- Symptoms: Weight gain (especially around the face, neck, and abdomen), high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar (leading to insulin resistance or Type 2 diabetes), thinning skin, easy bruising, muscle weakness, mood changes (anxiety, irritability, depression), fatigue, and irregular menstrual cycles in women.
- Too Little Cortisol (Hypocortisolism):
- Most commonly associated with Addison's Disease, a rare autoimmune condition where the adrenal glands are damaged and can't produce enough cortisol (and often aldosterone, another adrenal hormone).
- Symptoms: Chronic fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure, dizziness, muscle weakness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, joint pain, salt cravings, and darkening of the skin.
Managing Your Cortisol: Promoting Healthy Balance
Given cortisol's widespread influence, maintaining healthy levels is crucial for overall well-being. Here are some strategies:
- Stress Management: This is paramount.
- Mindfulness & Meditation: Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can significantly lower cortisol.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity is a great stress reliever, but avoid overtraining, which can increase cortisol.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Sleep deprivation is a major cortisol elevator.
- Time Management: Reduce overwhelm by setting realistic goals and boundaries.
- Social Connection: Spend time with loved ones; social support is a powerful buffer against stress.
- Hobbies and Relaxation: Engage in activities you enjoy to unwind.
- Nutrition:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods. Stable blood sugar helps regulate cortisol.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive intake can disrupt cortisol patterns.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water.
- Circadian Rhythm Support:
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at roughly the same time daily, even on weekends.
- Morning Light Exposure: Get natural light first thing in the morning to signal your body to wake up and start its cortisol cycle.
- Limit Blue Light at Night: Reduce screen time before bed to avoid disrupting melatonin production, which works inversely to cortisol.
- Medical Consultation:
- If you suspect a cortisol imbalance, consult a healthcare professional. They can perform tests (blood, urine, saliva) to assess your levels and determine the appropriate course of action.
Conclusion: Embracing the Balance
Cortisol is far more than just a "stress hormone"; it's an indispensable component of your body's intricate regulatory system. While acute stress responses are vital for survival, chronic elevation can chip away at your health. By understanding its functions, appreciating its delicate balance, and adopting proactive lifestyle strategies, you can empower yourself to manage stress effectively and foster optimal well-being. Listen to your body, and give it the support it needs to maintain this crucial hormonal harmony.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cortisol
Q1: Is cortisol always bad?
A: Absolutely not! Cortisol is essential for life. It helps you wake up, maintain energy, respond to danger, and regulate many bodily functions. It only becomes problematic when levels are consistently too high or too low for prolonged periods.
Q2: What are common symptoms of high cortisol?
A: Common symptoms include weight gain (especially around the abdomen and face), high blood pressure, high blood sugar, difficulty sleeping, fatigue, muscle weakness, mood changes (anxiety, irritability), and a weakened immune system.
Q3: Can stress really increase my cortisol levels?
A: Yes, absolutely. Both physical and psychological stress are primary triggers for cortisol release. Chronic, unmanaged stress is a major contributor to chronically elevated cortisol levels.
Q4: How can I naturally lower my cortisol levels?
A: Focus on stress management techniques (meditation, deep breathing, yoga), ensure adequate sleep, engage in moderate exercise, maintain a balanced diet, limit caffeine and alcohol, and seek social support.
Q5: What's the difference between natural cortisol and steroid medications?
A: Natural cortisol is produced by your adrenal glands. Steroid medications (like prednisone or hydrocortisone) are synthetic forms of cortisol. While they mimic cortisol's anti-inflammatory effects and are vital for treating certain conditions, long-term use can lead to similar side effects as chronically high natural cortisol.
Q6: Why is cortisol higher in the morning?
A: Cortisol levels naturally peak in the early morning as part of your circadian rhythm. This helps you wake up and provides your body with the energy boost needed to start the day. Levels then gradually decline throughout the day, reaching their lowest point at night to prepare you for sleep.
Q7: Can diet affect cortisol?
A: Yes, diet can influence cortisol. A balanced diet with stable blood sugar helps. Conversely, diets high in sugar, refined carbs, and excessive caffeine can potentially contribute to cortisol dysregulation. Nutritional deficiencies can also play a role.
[MEDICAL DISCLAIMER - TO BE ADDED BY YOU/MEDICAL PROFESSIONAL]
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog post is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health or starting any new treatment plan or dietary changes. Individual results may vary.
If you require any assistance with this article, please do not hesitate to Contact Us