Warning: Contains language and images that some may find offensive.
The clitoris is a small but powerful organ that plays a crucial role in female sexual pleasure and sensitivity. This document explores the anatomy of the clitoris, its functions, and its significance in sexual experiences. Understanding the clitoris is essential for enhancing sexual pleasure and fostering a deeper connection between partners.
The clitoris also plays a significant role beyond pleasure; it is vital for sexual arousal and overall reproductive health. Its ability to respond to touch and stimulation helps facilitate lubrication and prepares the body for sexual activity. Moreover, the clitoris serves as an indicator of arousal and emotional connection, often responding to psychological stimuli such as intimacy, trust, and comfort. Recognizing the importance of the clitoris in these broader aspects can deepen understanding of female sexuality and promote more respectful and attentive sexual interactions. Understanding its role as both a physical and emotional center can contribute to healthier, more satisfying intimate relationships.
Anatomy of the Clitoris
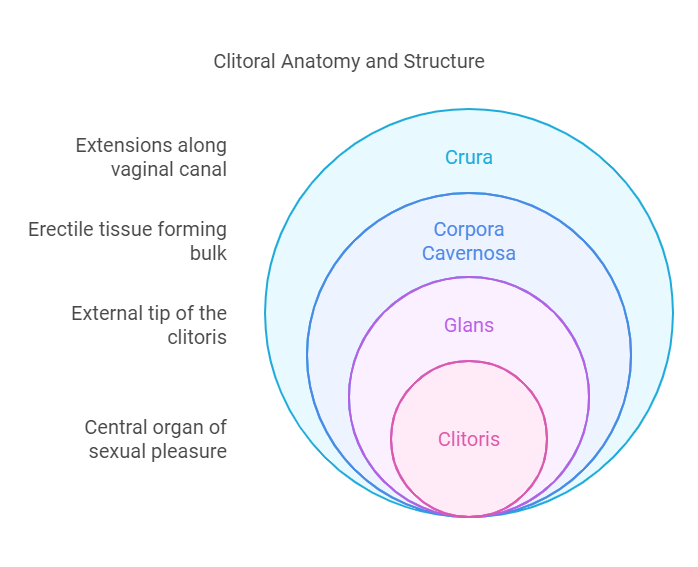
The clitoris is often described as a small, external structure located at the top of the vulva, but its anatomy is much more complex. It consists of erectile tissue, similar to that found in the penis, and extends internally into the pelvic region. The visible part, known as the glans, is just the tip of the iceberg; the majority of the clitoral structure is hidden beneath the skin. This internal network includes two corpora cavernosa and a crura that extend along the vaginal canal, contributing to sexual arousal and pleasure.
The internal structures of the clitoris also play a significant role in sexual response. Beyond the visible glans, the roots of the clitoris extend internally and surround the vaginal canal, forming a network that contributes to sensation in surrounding areas such as the vulva and perineum. Stimulation of these internal components can be equally, if not more, pleasurable than external touch. Furthermore, the ability of the clitoris to swell and become more prominent during arousal enhances the overall experience, making physical intimacy more responsive and engaging. Recognizing the importance of both external and internal stimulation allows for more nuanced and satisfying sexual interactions, emphasizing that the clitoris is not just about external pleasure but an intricate structure designed to heighten intimacy and connection.
Sensitivity and Pleasure
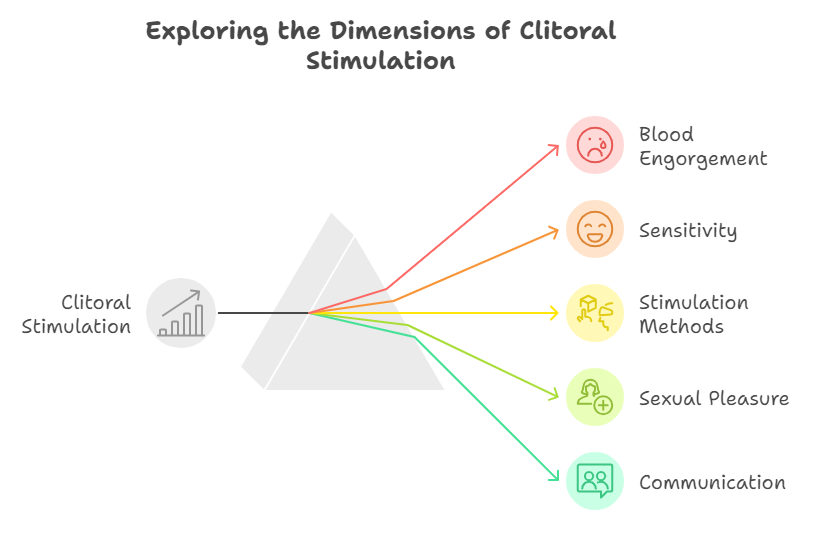
This body part is densely packed with nerve endings—approximately 8,000—making it one of the most sensitive areas of the human body. This high concentration of nerve endings is primarily responsible for the intense pleasure many women experience during sexual stimulation. The clitoris is designed for pleasure, and its stimulation can lead to orgasm, which is often described as a peak of sexual pleasure.
The Role of the Organ in Sexual Experiences
During sexual arousal, the clitoris becomes engorged with blood, increasing its sensitivity. Stimulation of the clitoris, whether through direct contact or indirect stimulation during penetrative sex, can enhance sexual pleasure for many women. Understanding the importance of clitoral stimulation can lead to more fulfilling sexual experiences, as it allows partners to explore what feels good and to communicate openly about their desires.
Conclusion
The clit is a vital component of female sexual pleasure and sensitivity. Its complex anatomy and high sensitivity make it a key player in sexual experiences. By recognizing and understanding the role of the clitoris, individuals and couples can enhance their sexual relationships, leading to greater intimacy and satisfaction. Emphasizing clitoral stimulation in sexual encounters can foster a more pleasurable and fulfilling experience for all involved.
The content of this post is provided for informational purposes only. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions regarding your health or wellness. The author is not a licensed medical professional, and this information should not be considered medical advice.
If you need any further information or assistance with this article, don't hesitate to Contact Us
Karen Blake
BAHN-NLP
TFT-DX